Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder Analysis
features:
| Time | Difficulty | People |
 |  | |
| Hours | Straightforward | Researcher |
intro:
The stakeholder analysis provides an overview of relevant people, organizations or industries who may influence or is influenced by an innovation. Map the stakeholders and develop an understanding of their role and perspectives related to the innovation you are working on. This helps you to better understand technological requirements and impacts, provides directions to increase acceptance of the innovation, and may indicate new opportunities.
steps:
 List all stakeholders1As an inspiration, you may consider which groups of people or organizations are involved in the use, production, supply, maintenance, distribution, disposal, financing, regulation, or standardization of the technology, as visualized in the socio-technical configuration. Make sure, you are not too quickly satisfied with noting the most obvious groups only. You may also distinguish between enactors and selectors, as these typically have rather different views on a technology:
List all stakeholders1As an inspiration, you may consider which groups of people or organizations are involved in the use, production, supply, maintenance, distribution, disposal, financing, regulation, or standardization of the technology, as visualized in the socio-technical configuration. Make sure, you are not too quickly satisfied with noting the most obvious groups only. You may also distinguish between enactors and selectors, as these typically have rather different views on a technology:-
- Enactors are stakeholders who are actively supporting or working on a technology: typically this may be technology developers, researchers, investors, shareholders, research institutes or clusters, technology firms, industrial partners, suppliers
- Selectors are stakeholders who see your technology as one of multiple options to choose from or pay attention to: this could be users, policy makers, funding agencies, investors, regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA, EMA), critical consumers, NGOs
- Some stakeholders may have an indirect role, but who are still affected by an innovation, and some of them may take an active position for or against a technology: affected residents, community organizations, special interest groups, excluded users or users of alternative technologies, competitors, people affected down the supply chain or by disposal, or ‘stakeholders’ without a voice (nature, the Northern Sea, an animal species etc.)
-
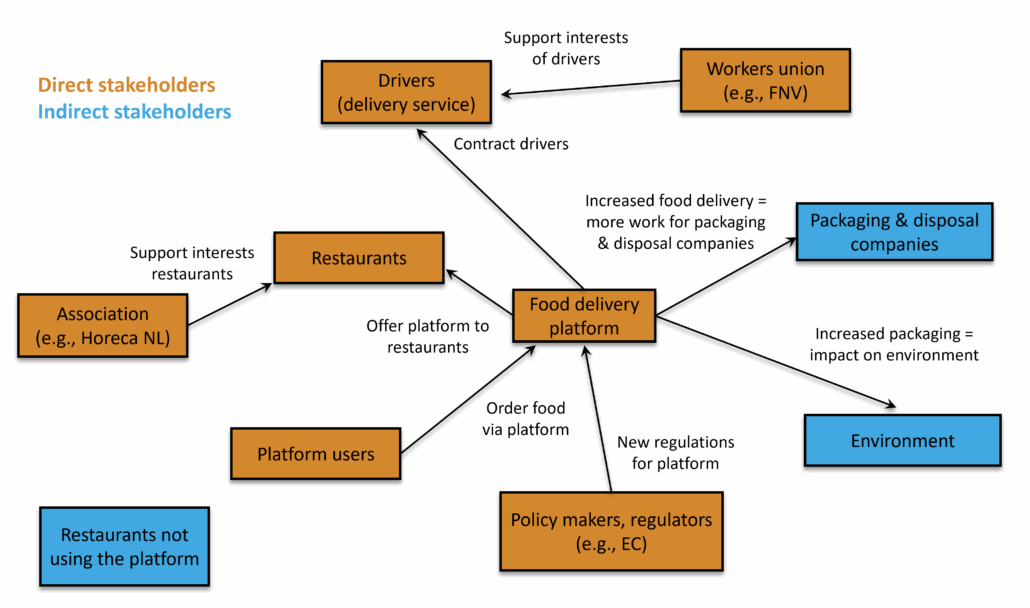
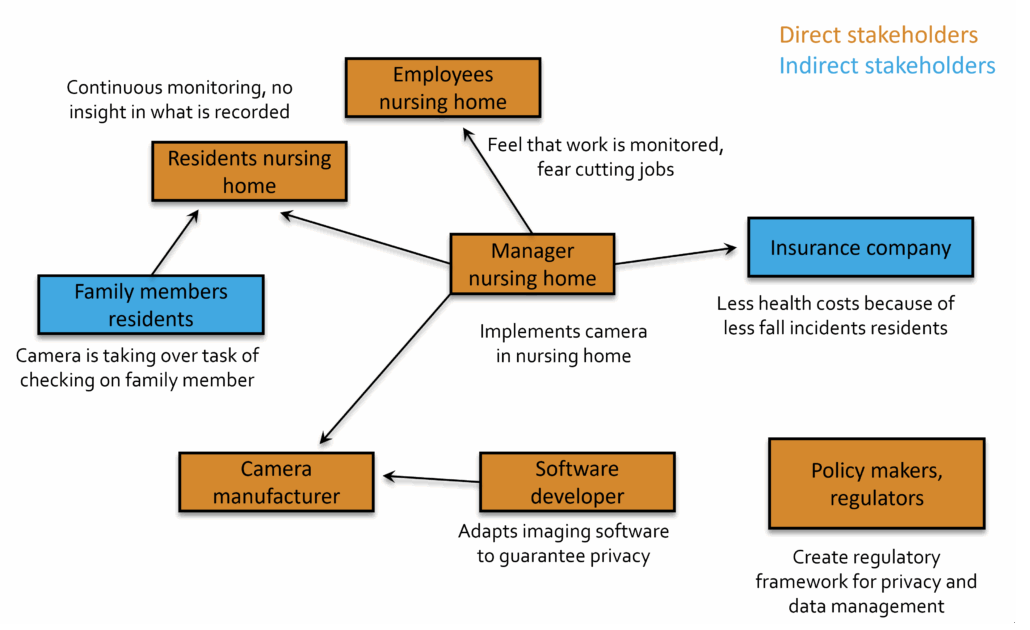
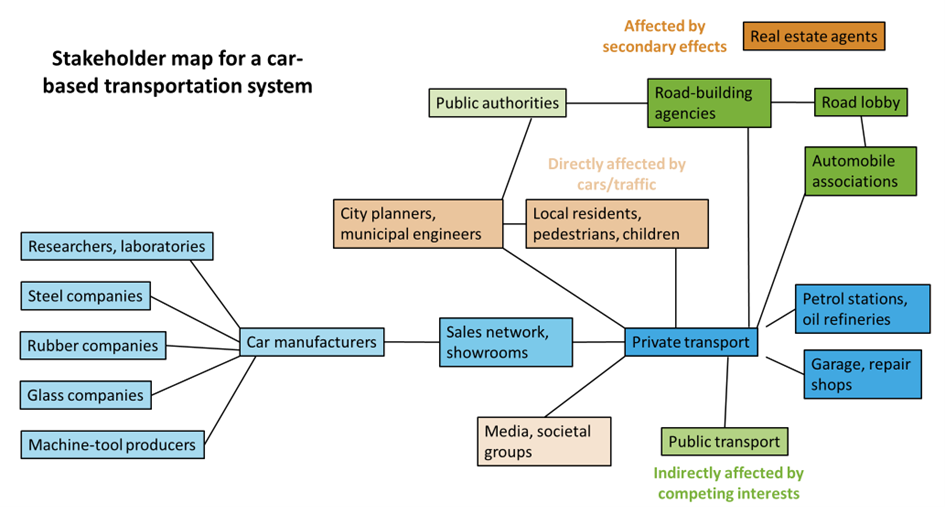
 Mapping2Create a figure that shows the stakeholders and their relations. This figure provides you with an overview of the most relevant stakeholders and allows you to identify the stakeholders who are directly or indirectly influenced by the new innovation.
Mapping2Create a figure that shows the stakeholders and their relations. This figure provides you with an overview of the most relevant stakeholders and allows you to identify the stakeholders who are directly or indirectly influenced by the new innovation.
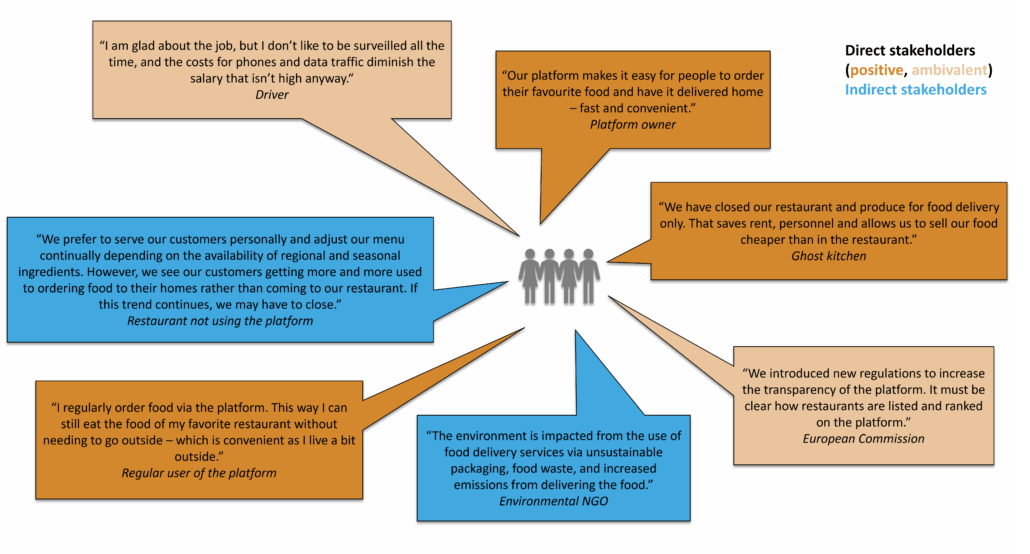
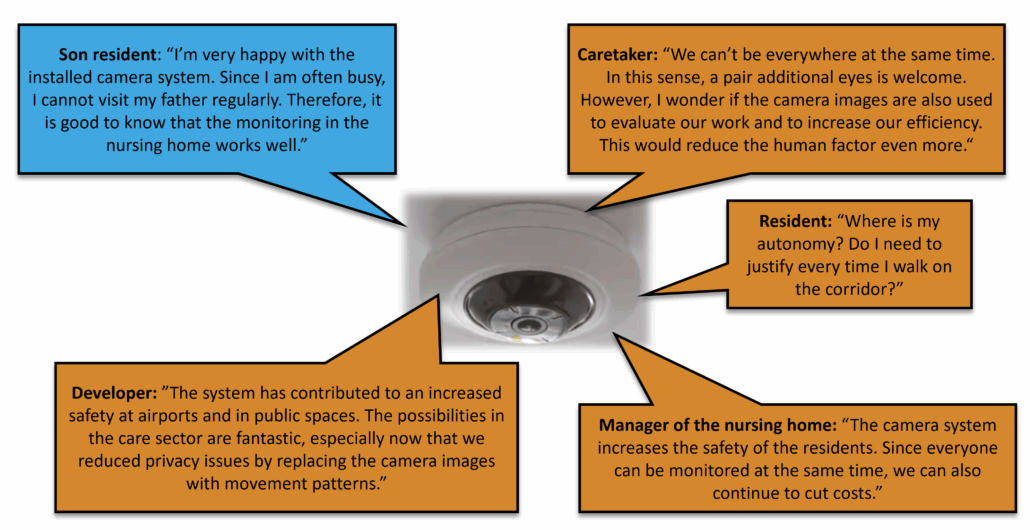
 Position and perspectives3You should then search for information that helps to better understand the role and needs of a particular group with regards to a technology, relevant statements, actual activities or explicit strategies. Which stakeholders may appreciate certain features of the innovation or have a critical perspective on them? Who may affect your innovation positively or negatively? If possible, get in contact with the most relevant stakeholders to better understand their perspective on this particular innovation. If there is no better information available, you may imagine yourself in the position of the stakeholders and anticipate on their perspective with respect to your technology.
Position and perspectives3You should then search for information that helps to better understand the role and needs of a particular group with regards to a technology, relevant statements, actual activities or explicit strategies. Which stakeholders may appreciate certain features of the innovation or have a critical perspective on them? Who may affect your innovation positively or negatively? If possible, get in contact with the most relevant stakeholders to better understand their perspective on this particular innovation. If there is no better information available, you may imagine yourself in the position of the stakeholders and anticipate on their perspective with respect to your technology.